Since its launch on July 30, 2015, Ethereum has been using a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to secure its network. The PoW mechanism involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to create new blockchain blocks. This process allows Ethereum nodes (distributed computers) to agree on transaction requests and prohibit manipulation. However, Ethereum switched from PoW to a proof of interest (PoS) mechanism on September 15, 2022.
The transition from PoW to PoS split the Ethereum network into EthereumPoW and Ethereum. This article takes you through EthereumPoW, why EthereumPoW hard forks happen, ETHW vs. ETH, ETHW vs. ETC, and if EthereumPoW will succeed.
What is Ethereum PoW? EthereumPoW (ETHW), the proof-of-work (PoW) offshoot of Ethereum, is a community project for sovereign developers and miners led by crypto industry veteran Chandler Guo. Guo proposed the idea of ETHW on Twitter on July 27, 2022. Since then, The topic has attracted a lot of attention, especially from miners who oppose The Merge. Even Tron founder and Poloniex investor Yuchen Sun campaigned for the project to support PoW mechanisms on Ethereum and offered to donate some forked ETHW to build the ecosystem.
However, after the merger, Poloniex ended up supporting another fork called EthereumFair (ETHF).
ETHW core contributors publish a Twitter thread that contains the main network activation roadmap for the ETHW mechanism. According to The plan, The main web will go live a few hours after The Merge, The transition from PoW to PoS. In addition, the main network will be activated in the 2,049th block epoch after the change. This is why ETHW's block height will always be The Merge +2,048 height. Initially, it will have an average mining difficulty of about 220 transactions, while the hash rate will exceed 15 transactions per second (TPS).

Here is the ETHW main network information:
The network name is ethw-mainnet.
The new RPC URL -- https://t.co/MQ04pnPQyW
Chain ID - 10001
Currency symbol - ETHW
Block browser URL -- https://t.co/J3JllmQA8I
Why does EthereumPoW hard fork Happen?
Before we dive into why EthereumPoW has hard forks, let's understand what hard forks mean. A hard fork is a blockchain software upgrade that requires all network verifiers to adhere to the latest version of the network software. While Ethereum has experienced multiple hard forks before, the most significant one occurred in 2016 when it split into Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC).
The EthereumPoW hard fork happened because some miners didn't want to give up the lucrative PoW mechanism in exchange for less profitable PoS. According to the latest report from Arcane Research, Ethereum mining revenue reached $18 billion in 2021, slightly ahead of Bitcoin's $17 billion return. Even in the second half of 2022, Ethereum miners have been the top earners. The chart below compares the mining rewards of the two most important digital currencies by market capitalization over the past two years.
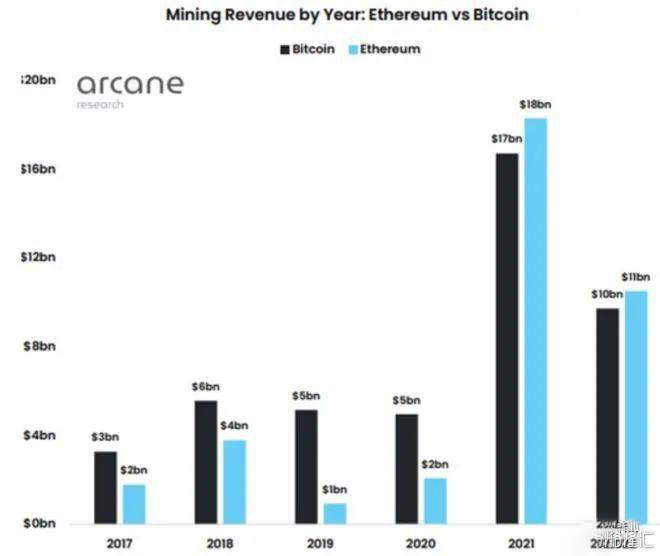
As the chart shows, Bitcoin's mining revenue was higher than Ethereum's until 2021. With revenues reaching billions of dollars, Ethereum miners have invested heavily in high-end mining equipment to boost their earnings. However, those gains immediately disappeared as Ethereum moved from PoW to PoS. That's why some miners have vowed to continue using PoW mechanisms on the Ethereum network.
In a PoW network, miners confirm trades and compete with each other to solve mathematical puzzles. The PoS network, on the other hand, excludes miners. Instead, investors pledge their tokens to protect the network and do not need mining equipment. An algorithm randomly selects the pledgee to determine the next block, and the larger the pledgee, the greater the chance of being selected. The main benefit of the PoS network is that it is more energy efficient compared to the PoW blockchain.
Will EthereumPoW succeed? A blockchain fork requires copying all existing features, wallet balances, assets, and smart contracts. This means that all assets running on Ethereum will now run on the EthereumPoW main network. However, this is unwise without the support of the community. When the network splinteres, users identify the "real" chain by looking for value. For EthereumPoW to succeed, it will require broad support from everyday crypto users, developers, and businesses -- not just miners. Without these three groups, ETHW would be useless, like a discounted photocopy of the Mona Lisa.
However, this is unlikely to happen, mainly because of Ethereum's extensive ecosystem. Ethereum's ecosystem includes thousands of standalone assets, DeFi markets, NFTS, and staboins.
Adding stablecoins to ETHW is more complicated because stablecoins are backed by real-world assets, such as dollars in a bank account. That means unless you're the Fed, it's almost impossible to fork off such assets without depositing collateral with a financial institution.
For example, Tether (USDT), the largest stablecoin by market capitalization, has taken these questions into account. Paulo Ardoino, its chief technology officer, said the company would only support the merged Ethereum. USDT accounts for billions of dollars in Ethereum. EthereumPoW would face some challenges without Tether's support. Ardoino said the complexity of DeFi guided their decision.
Aave, the largest DeFi lending protocol on Ethereum, also has a say, with head of integration Marc Zeller highlighting Ardoino's point. "You can't have a legally backed stablecoin that doubles supply overnight and maintains the value of $1." He further explained that stablecoins can limit the success of any fork, and that the best way forward is to issue new stablecoins -- again downplaying the nature of the fork.
For a quick look at the different Ethereum forks and blockchains, you can check out the Eth Wars page on the Gecko terminal, which summarizes the price of the different tokens, the 24-hour price change, the dominance, and how it compares to the market capitalization of Eth.
ETHW call data replay vulnerability On September 16, EthereumPoW suffered a replay bug that resulted in 200 ETH being stolen by hackers. Two days later, blockchain security firm BlockSec revealed the incident, saying the attack occurred via Omni Bridge on the Gnosis chain.
A replay vulnerability is a cyber attack in which a hacker pauses or dishonestly replays a trade message on another network to execute a single trade two or more times. For the ETHW call replay vulnerability, the attacker first transferred 200 parcels of Ethereum (wETH) through the Gnosis chain Omni Bridge, and then replayed the transaction on the EthereumPoW blockchain for an additional 200 wETH. The attack depleted the balance of contracts running on the network.
While acknowledging the attack, the ETHW team released raw data showing that the two transactions were completely different and therefore refused to replay the transactions on the network. Instead, it clarified that the attack was a unit data replay due to a vulnerability in the Omni Bridge contract.
ETHW and ETH ETHW is the native token of the EthereumPoW network, while ETH is the native currency of Ethereum. Here's how the two tokens compare:
Changes in the consensus mechanism After transitioning to the PoS mechanism, the Ethereum network randomly picks an ETH verifier and gives them the responsibility of determining the next block. To become an individual verifier, you must pledge at least 32 ETH. If you have fewer than 32 ETH and want to participate in the ETH pledge, you can join the pledge pool. To protect the network from scams and fraud, verifiers who verify fraudulent transactions are fined - a process known as forfeiture.
In addition to being sustainable, PoS consensus has helped Ethereum become more decentralized than EthereumPoW. Moreover, the verifier no longer has to buy expensive mining equipment. Even if they don't hold 32 ETH to join as individual verifiers, ETH holders can pledge their tokens through the mine pool to protect the network, and more participation leads to more decentralization.
Shard Another important update that sets ETH apart from EthereumPoW is sharding. Sharding is a programming process in which data is distributed to multiple computers to increase processing speed. Ethereum will take advantage of sharding by introducing 64 sharding. Each shard is like a new chain, linked to the previous Ethereum network, integrated with previously recorded transactions. Ethereum and EthereumPoW work similarly, except ETH distributes the workload across multiple databases.
Sharding will directly address Ethereum's scalability issues. Unlike EthereumPoW, which processes only 15 TPS, ETH will become much more efficient, processing close to 100,000 TPS. You can think of EthereumPoW as a single-lane busy street, while ETH has a multi-lane busy road. The extension allows traffic to flow seamlessly and increases the speed at which vehicles can move.
However, Sharding is only expected to ship in 2023-2024.
Beacon chain We've already discussed how Ethereum introduces 64 shards and how validators are selected to validate blocks. However, something should connect the shard and identify the verifier. This brings us to the final significant difference between ETHW and ETH. The 64 shards are integrated into a single blockchain that controls them and facilitates transactions. Thus, the blockchain acts as the brain of the entire ecosystem, known as the beacon chain.
The beacon chain was launched in 2020 to ensure that the PoS mechanism is functional and sustainable before it is officially implemented. Therefore, it runs with the original PoW chain. But after The Merge, it began to act as The backbone of ETH.
Another role of the beacon chain is to randomly select verifiers and monitor their activity. The chain is also responsible for punishing verifiers who try to verify illegal transactions. Randomness in the selection of verifiers is necessary to ensure that the network does not favor certain actors over others.
ETHW and ETC Despite sharing the same chain (the Ethereum main network), the values of ETHW and ETC differ greatly. At the time of writing, ETHW was trading at $13.41 and ETC was trading at $34.43. Since ETC bifurcated from ETH in 2016, it has missed out on the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTS). ETHW, by contrast, is the newest branch of ETH. With the growth of DeFi applications developed over the past four years, ETHW could be more valuable than ETC if the entire community fully supports it.
conclusion The newest and hottest Ethereum fork -- EthereumPoW -- will benefit from The Merge. Through airdrops and charm incentives, the EthereumPoW team convinced nearly 20 former Ethereum mining pools to continue protecting the network. While the combined market may be suitable for using PoW Consensus's smart contract chain, some see ETHW as more of a cash grab. If EthereumPoW gets more community support, it will undoubtedly be more successful than Ethereum Classic.




